- TechOps Examples
- Posts
- Kubernetes Operator vs Controller - Which One to Choose?
Kubernetes Operator vs Controller - Which One to Choose?
TechOps Examples
Hey — It's Govardhana MK 👋
Welcome to another technical edition.
Every Tuesday – You’ll receive a free edition with a byte-size use case, remote job opportunities, top news, tools, and articles.
Every Thursday and Saturday – You’ll receive a special edition with a deep dive use case, remote job opportunities, and articles.
Kedify — just launched the advanced Kubernetes Autoscaling Playbook!
Real world architectures. Advanced configurations. Impactful visuals.
Pure practical insights for Kubernetes practitioners and tech leaders.
👀 Remote Jobs
Avalanche is hiring a DevOps Engineer
Remote Location: Worldwide
GitLab is hiring a Principal Security Engineer
Remote Location: Worldwide
📚️ Resources
Looking to promote your company, product, service, or event to 55,000+ Cloud Native Professionals? Let's work together. Advertise With Us
🧠 DEEP DIVE USE CASE
Kubernetes Operator vs Controller - Which One to Choose?
“What exactly is an Operator, and how is it different from a Controller?”
It’s a common question that comes up once you start automating Kubernetes workloads beyond the basics. Both aim to maintain desired state, but they operate at different scopes.
Controllers manage built in Kubernetes resources like Pods and Deployments.
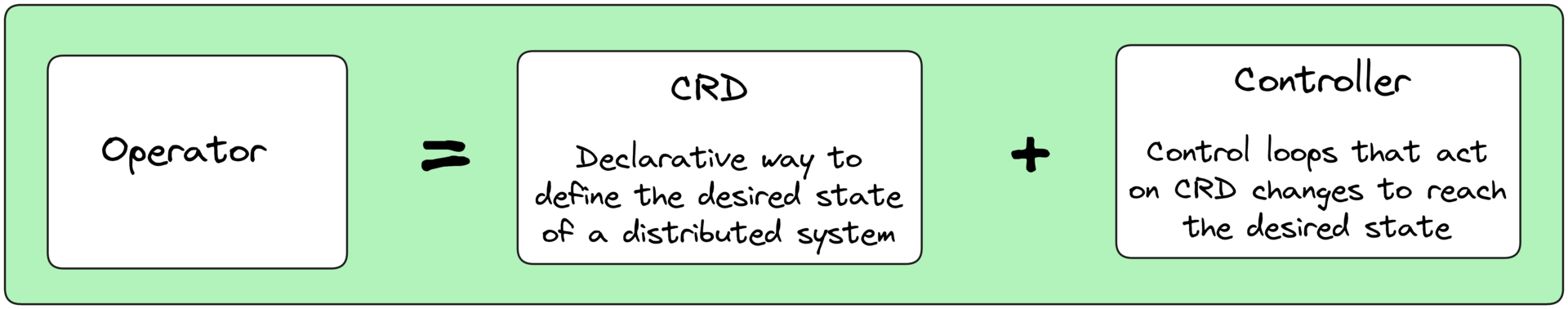
Operators manage custom, domain specific applications using Custom Resource Definitions and control loops.
Before diving into, let’s first understand what forms the foundation of an Operator.
How Kubernetes Controllers Work
Kubernetes controllers form the automation layer that keeps the cluster in its desired state. They constantly watch the system, detect drifts, and act to correct them. To understand how this works, we start with the core concept of Desired State and Current State, and then look at how the controller architecture enforces it.
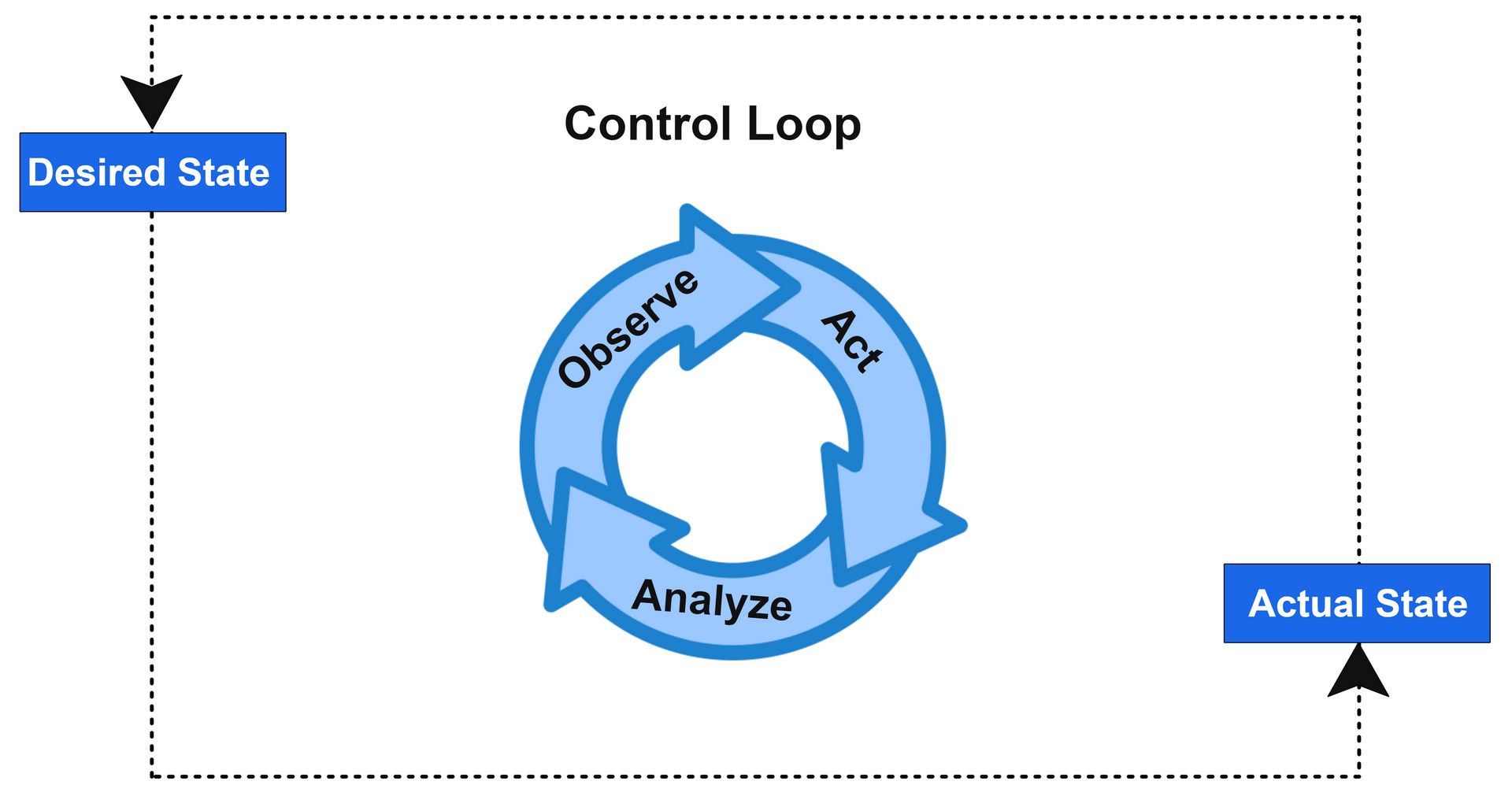
Desired State vs Current State
When you create a Kubernetes object such as a Deployment or Service, you define its desired state, for example “3 replicas of Nginx should be running.”
Kubernetes continuously compares this desired state with the current state, which represents what is actually running in the cluster. If there is a difference, the controller acts to reconcile it.
If one Pod is down, it creates a new one.
If extra Pods exist, it removes them.
If configurations differ, it updates them to match the definition.
This continuous reconciliation makes Kubernetes self healing and declarative.
Controller Architecture
A controller’s logic runs in the control plane and interacts closely with the API Server.
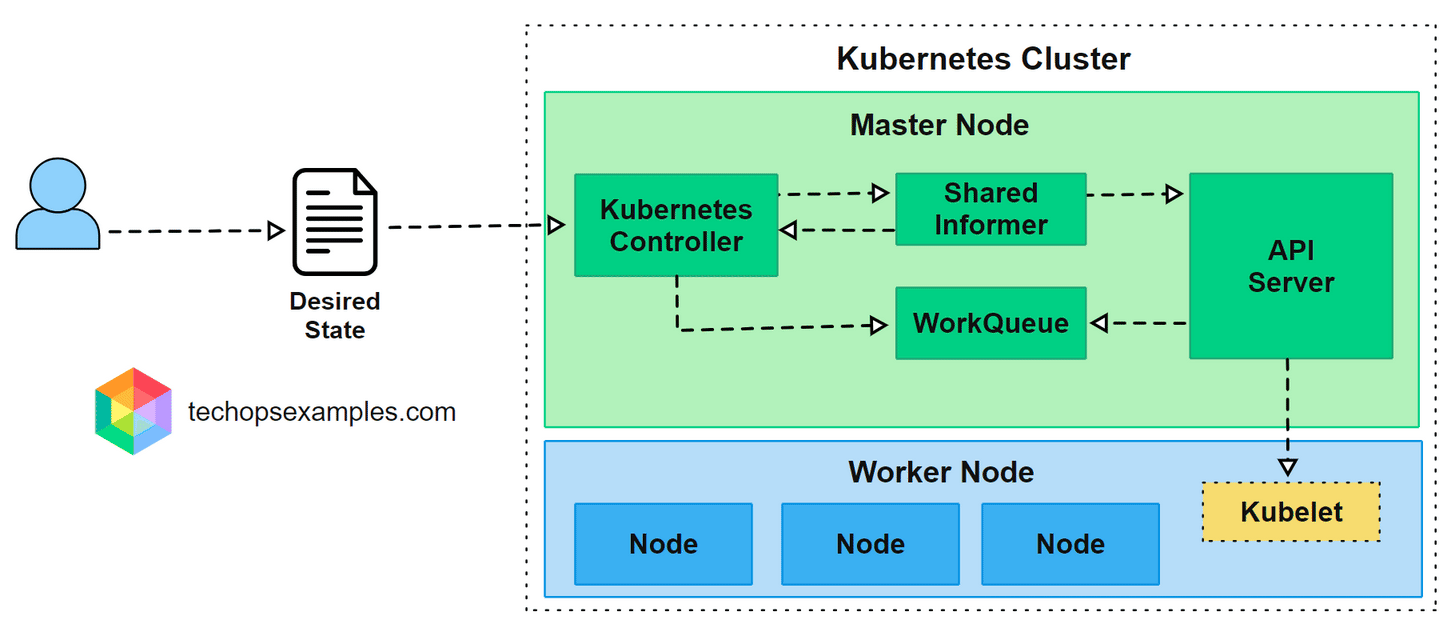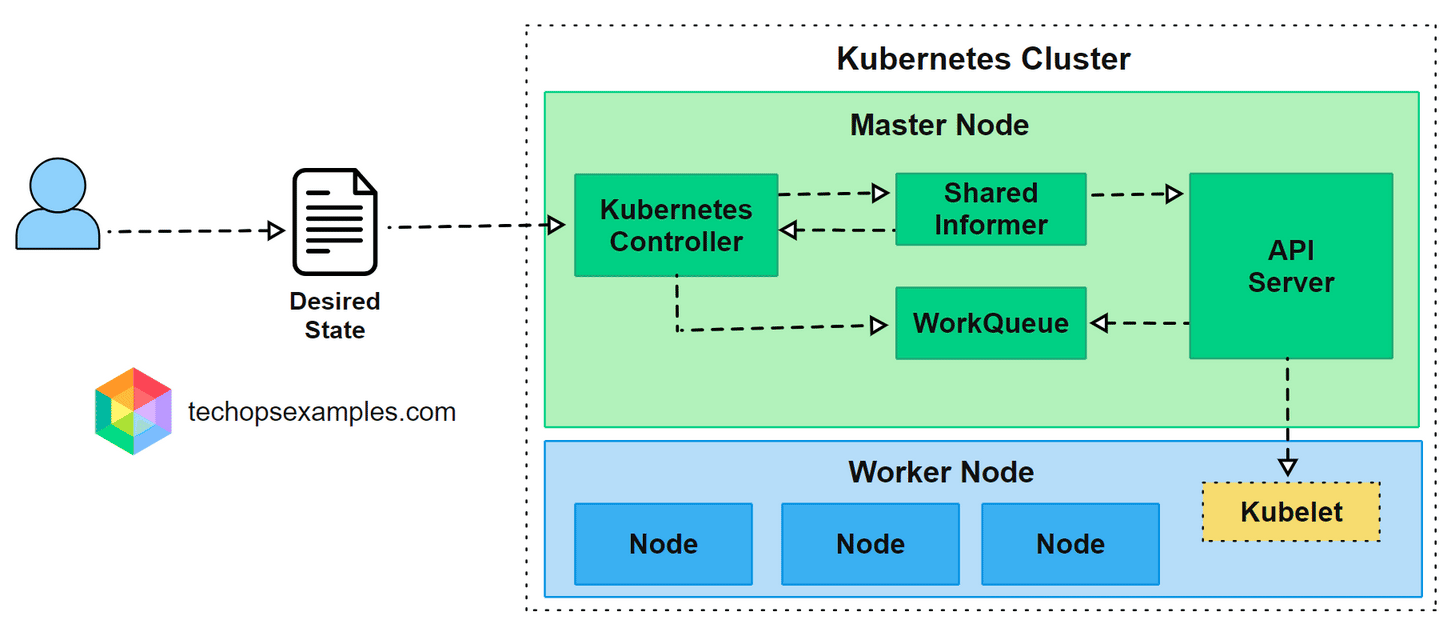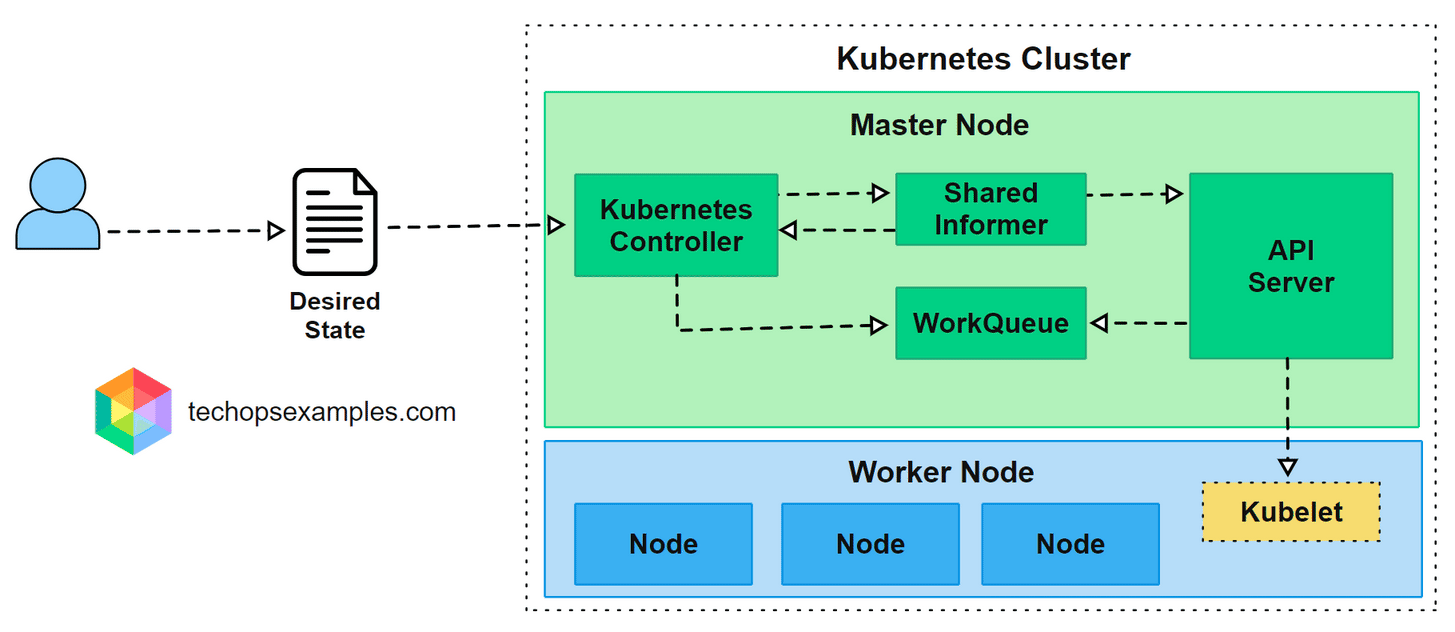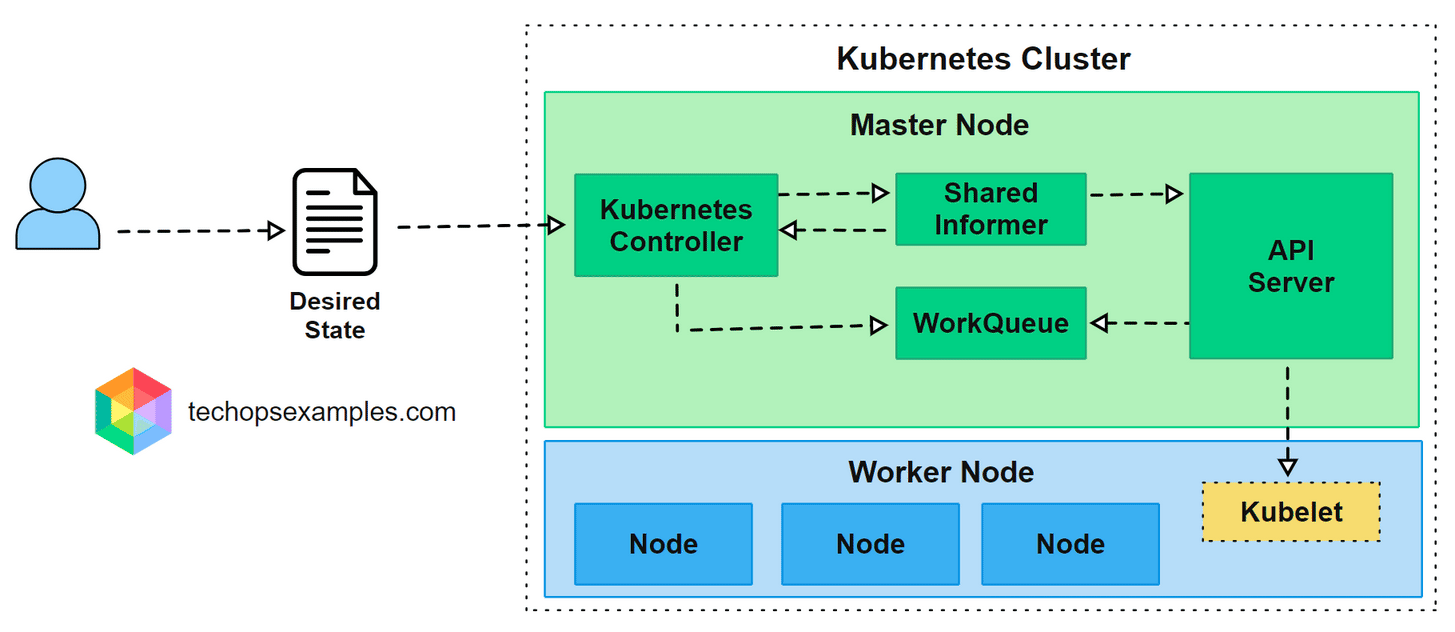
Here is how the workflow happens in practice:
User submits a manifest defining the desired state such as replicas, configurations, or resource limits.
API Server stores the object and makes it available to all cluster components.
Shared Informer watches for changes and keeps an updated local cache.
Controller processes the change and adds it to a WorkQueue for sequential handling.
Reconciliation loop runs to compare desired and current state and perform corrective actions through the API Server.
This loop operates continuously, ensuring the cluster remains stable even when workloads fail, nodes go offline, or configurations drift.
Test how your controller reconciles drift. Missed events or slow loops can silently break automation.
How Kubernetes Operators Work
Kubernetes Operators extend the controller concept to manage complex or domain-specific workloads by introducing Custom Resource Definitions (CRDs) and custom reconciliation logic.
While a controller manages native objects such as Pods or Deployments, an Operator brings the same lifecycle management to external or higher-level systems like databases, caches, or messaging clusters.
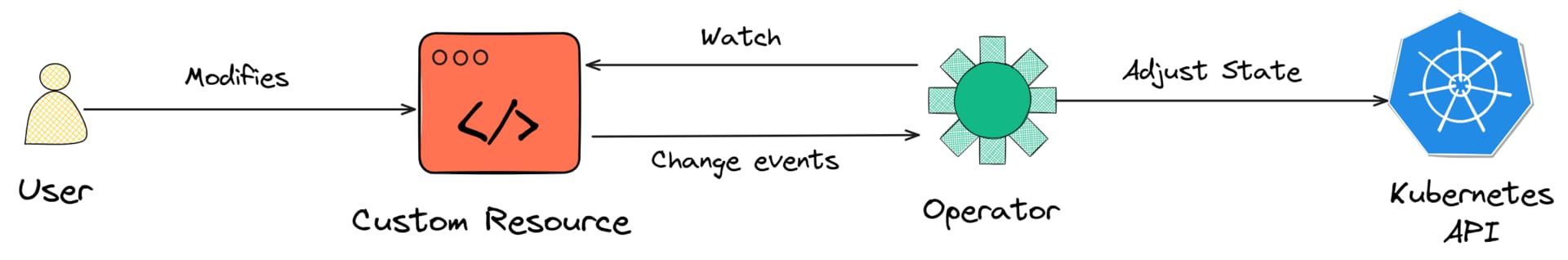
A CRD defines a new API resource type in Kubernetes. Once registered with the API Server, it behaves like a native object. For example, you might define:
apiVersion: "cache.techops.io/v1"
kind: RedisCluster
metadata:
name: redis-primary
spec:
replicas: 3
version: 7.0TOGETHER WITH THE HUSTLE DAILY
200+ AI Side Hustles to Start Right Now
AI isn't just changing business—it's creating entirely new income opportunities. The Hustle's guide features 200+ ways to make money with AI, from beginner-friendly gigs to advanced ventures. Each comes with realistic income projections and resource requirements. Join 1.5M professionals getting daily insights on emerging tech and business opportunities.

Upgrade to Paid to read the rest.
Become a paying subscriber to get access to this post and other subscriber-only content.
Already a paying subscriber? Sign In.
Paid subscriptions get you:
- • Access to archive of 200+ use cases
- • Deep Dive use case editions (Thursdays and Saturdays)
- • Access to Private Discord Community
- • Invitations to monthly Zoom calls for use case discussions and industry leaders meetups
- • Quarterly 1:1 'Ask Me Anything' power session


